Dermatology
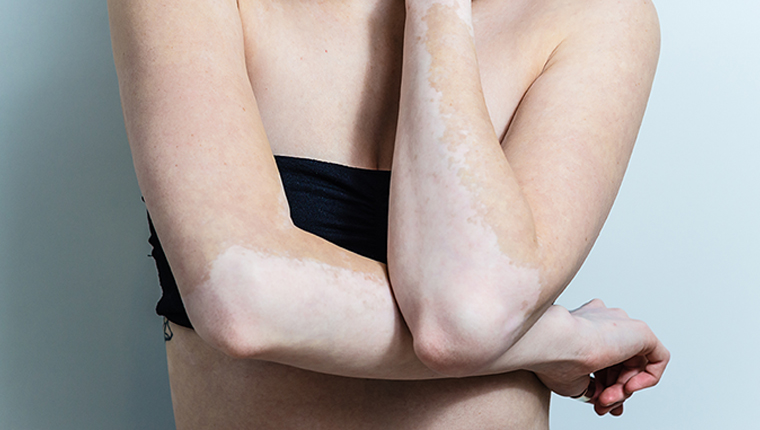
Vitiligo
It is an acquired skin pigmentation disorder resulting in the appearance of white blotches on the surface of the skin or mucous membranes at any time during life. It is caused by the progressive damage or inactivation of the melanocytes found in the deeper layers of the skin and are responsible for the coloring of its superficial cells.
Symptoms
The main sign of vitiligo is the loss of melanin that creates light-colored or white spots-patches on the skin. Usually, discoloration appears for the first time in areas of the body exposed to the sun, such as hands, legs, arms, face and lips. The initial stage of vitiligo is usually characterized by the occurrence of a plaque, often in the abdomen, and in some cases occurs with the onset of itching or hyperhidrosis. Sometimes vitiligo affects the scalp and hair.
The occurrence of vitiligo has often been associated with other diseases such as thyroid conditions (hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism or Hashimoto’s thyroiditis), as well as with rheumatoid arthritis or alopecia.
The changes in your appearance caused by vitiligo may affect your emotional and psychological wellbeing and may cause difficulties in your professional and social life. People with vitiligo may experience emotional stress, especially if vitiligo develops in visible parts of the body, such as the face, hands, legs, or genitalia. Adolescents, who are particularly concerned about their appearance, are emotionally affected by extensive vitiligo. Some people who have vitiligo feel embarrassed, shy, depressed, or worried about how others react when they see them.
Treatment
Vitiligo is localized, segmental and generalized. Usually, its diagnosis is made following clinical examination. A biopsy may be required in case of differential diagnosis from other conditions that cause hypoxia such as post-inflammatory hypopigmentation, mycosis fungoides and varieties of tinea versicolor. Sometimes people with vitiligo ignore its importance and do not know how to treat it. The treatment of vitiligo should be tailored to the patient, considering the benefit of the treatment in relation to the possible side effects of each type of treatment. The results of the treatments currently available vary and can not guarantee complete repigmentation of the area.
LP Clinic applies an innovative treatment method for healthy skin transplantation, small in size from 1mm to 1.5mm, at the vitiligo sites to restore melanocytes. This treatment can be effective for 90 to 95% of patients.
A. It can be applied to localized lesions provided that the condition has stable and has not spread for at least 6 months. You should have made an appointment with our dermatologist for a complete clinical examination and medical history taking.
A. Vitiligo is not an infectious or contagious disease, therefore it cannot be transmitted by physical contact or body fluids from the person suffering from it to other healthy individuals.
A. While there is a greater likelihood for a child to manifest vitiligo if the gene responsible for its occurrence is present in family history, however, vitiligo is not considered as a heritable disease.
A. In order to protect and prevent the spreading of white patches, it is necessary to avoid injuries to prevent the occurrence of new lesions and to systematically use sunscreen for protecting white areas due to absence of melanin and for protecting normal skin against burns where new vitiligo lesions may develop.